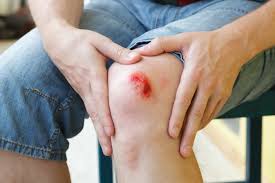
Skin injuries are common and can range from minor cuts and abrasions to severe lacerations and burns. These injuries disrupt the integrity of the skin, which acts as a barrier against infection and environmental hazards. Proper treatment is crucial to ensure healing and prevent complications.
Skin injuries refer to any damage or trauma to the skin. They can be classified into various types, including:
The treatment procedure depends on the type and severity of the skin injury:
While nebulizers are not applicable for skin injuries, alternative treatments and aids include:
By understanding the nature of skin injuries and following appropriate treatment protocols, you can ensure effective healing and reduce the risk of complications.
© 2021-2025 Wyandotte Urgent Care Clinic. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.