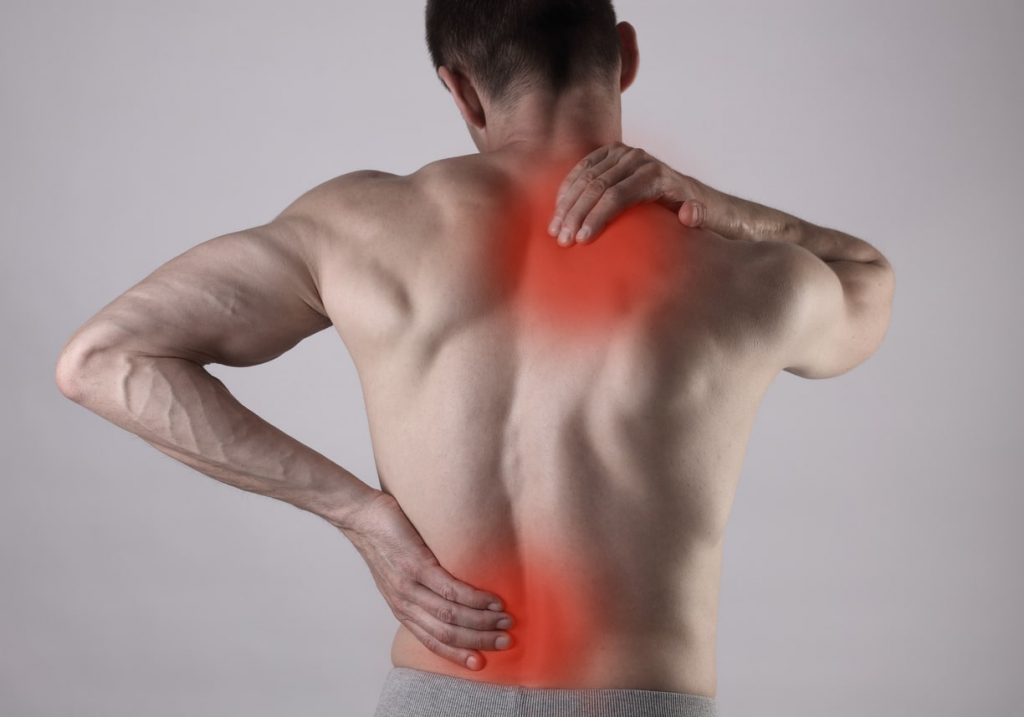
Muscle spasms, also known as muscle cramps, are involuntary contractions of one or more muscles. They can be sudden and painful, often occurring in the legs, arms, back, or other muscle groups.
Muscle spasms are involuntary and often painful contractions of a muscle or group of muscles. They can occur for various reasons, including overuse, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, or underlying medical conditions. Common triggers include strenuous exercise, poor posture, or staying in one position for too long.
Treatment for muscle spasms typically involves:
Nebulizers are not used for muscle spasms. Alternatives and treatments include:
Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition and symptoms.
© 2021-2025 Wyandotte Urgent Care Clinic. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.