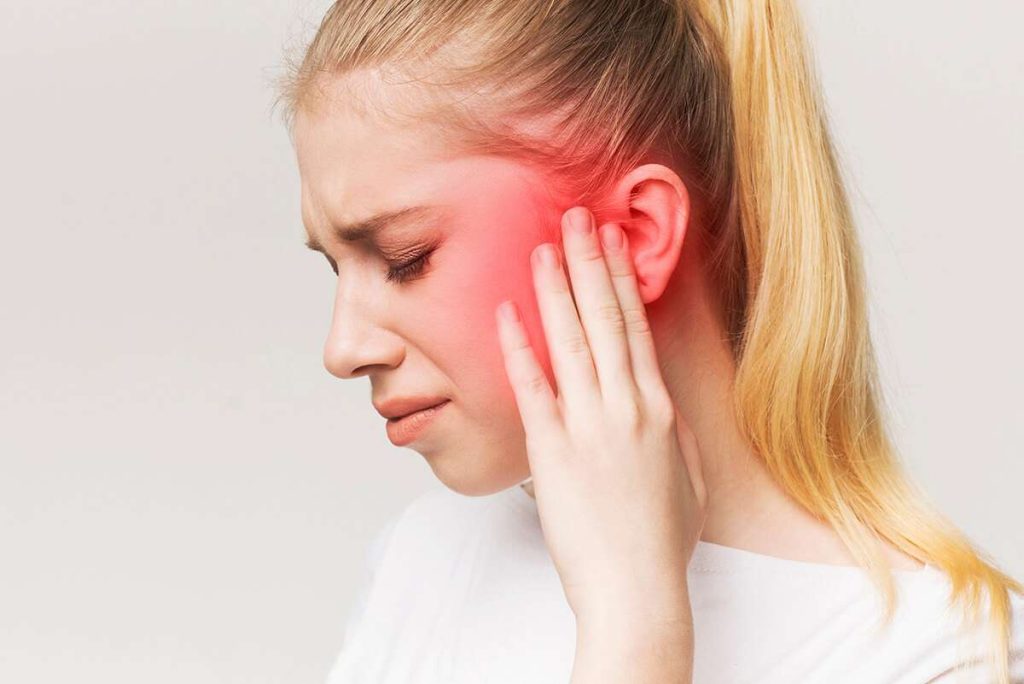
Ear ache, or ear pain, is a common symptom that can result from various conditions affecting the outer, middle, or inner ear. It can be a sharp, dull, or burning pain and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as hearing loss, discharge, or dizziness. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for relief and […]
Ear ache, also known as otalgia, is pain located in the ear. It can be caused by infections, injuries, or referred pain from other areas such as the throat or jaw. Ear infections, fluid buildup, and eustachian tube dysfunction are common causes of ear pain.
When evaluating ear ache, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough examination, which may include:
While nebulizers are generally used for respiratory conditions and not directly for ear aches, treatment options for ear pain include:
Understanding the causes of ear ache and the available diagnostic and treatment options can help individuals manage their symptoms effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
© 2021-2025 Wyandotte Urgent Care Clinic. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.