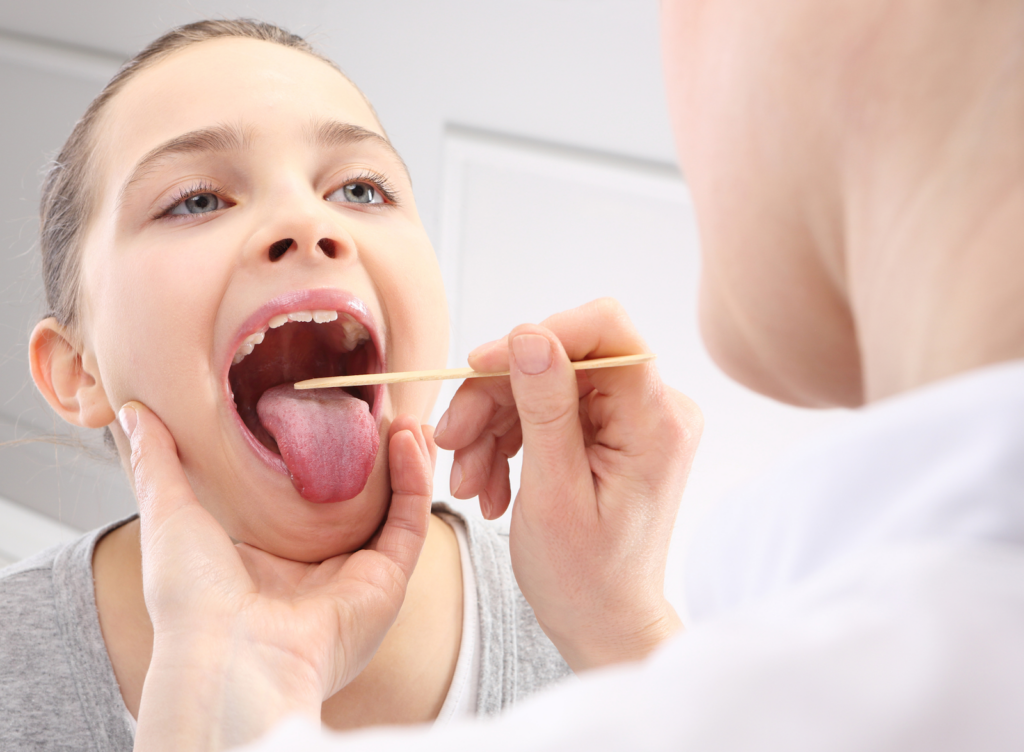
A strep test is a diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of Streptococcus bacteria, specifically Group A Streptococcus (GAS), which causes strep throat. This test helps to diagnose and treat strep throat, preventing complications and the spread of infection.
A strep test is a medical test used to determine if a sore throat is caused by a Group A Streptococcus (GAS) infection. It involves taking a throat swab to detect the presence of the bacteria. There are two main types of strep tests: the rapid strep test and the throat culture.
The process of performing a strep test typically involves the following steps:
© 2021-2025 Wyandotte Urgent Care Clinic. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.